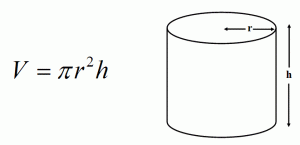6.G.A.4: Solve real-world and mathematical problems involving area, surface area, and volume.
Tasks: Students will have to properly use the equations provided in order to calculate the surface area and volume of the following shapes.
When calculating the surface area of an object (examples 1, 2, and 4) how many faces are there in order to get the right answer?
Commentary
The goal of this task is for students to understand the concepts behind 3D shapes and have a visual representation of shapes. During the lesson is taken place, the teacher will require to show students how to properly label the parts of the shape in order to correctly use the information in the equations provided to them. This will allow the students to understand the different dimensions and sides of a shape. Once the students are able make connections, the students will be able to determine the surface are and volume of a shape. With this being said, it’s common that students make simple mistakes such as forgetting to add the right number of faces of a shape. At this point, the teacher will need to use this task to make sure that students are able to understand the dimensions of a figure and how they differ from a different shape. The teacher will provide the properties and cover example problems in order to calculate the surface are of the shapes and volume. The students will also have a visual representation of the shapes.
Solution:
- By looking at the shape, we can see that there are four faces/sides with the same dimension of 3×2. This implies that the dimension of 3×2 will be multiply by 4 or simply add (3×2=6) 4 times. This will result of 24 in². The remain 2 faces/sides have a dimension of 2×2 resulting in 8 in². To a total surface are of 32 in².In order to calculate the volume of the figure (Length x width x height) we get 2in * 3in * 2in = 12 in³.
- To calculate the surface area of this shape, the same procedure as solution 1 will be follow with the exception that in order to calculate the surface area of triangle will require the equation of (base*height)/2. To a total surface area of 29.6 in². In order to calculate the volume of shape the picture on the right illustrate the equation needed to do so and volume = 8 in³.

- In order to calculate the volume of a cylinder the picture on the left illustrate how to do it. The volume of the shape will be 230.91 in³. To calculate the surface area of the cylinder, it will require students to use the equation. Surface area = 209 in².
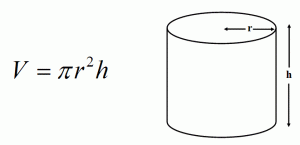
- In order to calculate the surface area, we can see that the shape has a right triangle and two of the faces make up a square resulting in 49 in². By adding to other 3 sides/faces we get a total of 240.2 in². To calculate the volume of the figure the equation of Volume = area of base x height will be needed. This indicates that area of the base is (7*7)/2 and the height is 8 in where the volume = 196 in³.