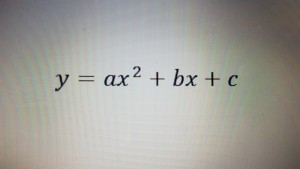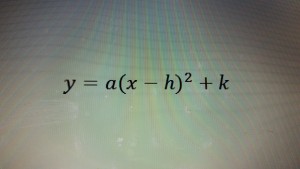Basketball, soccer ball, racquetball, bouncy ball; what child does not like to play with a ball!?
So why not have a math lesson that appeals to their interest of bouncing balls!
Picture a bouncing ball. As the ball makes contact with the floor, the ball rises and slows, then descends and speeds up. For any one of those bounces, the ball’s height can be plotted as a function of time, making a parabolic shape. Therefore, the relationship between the height and time for any bounce of the ball is a quadratic.
The relationship between the graph and the bouncing ball is expressed as
where y is representing the height of the ball at any given time x. Another form of the quadratic equation is
where h is the x-coordinate of the vertex, k is the y-coordinate of the vertex, and a is a parameter. This form of the quadratic equation is called the vertex form.
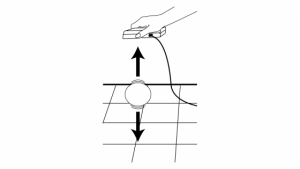
In this activity, students will use a Motion Detector, along with a TI-Nspire, to record the motion of a bouncing ball. Once the students have collected the data, they will analyze the data and model the ball’s height as a function of time during one bounce using the standard quadratic equation, as well as the vertex form of the quadratic equation.
This activity’s objective meets two of the Common Core State Standards:
- MATH.CONTENT.6.EE.C.9
Use variables to represent two quantities in a real-world problem that change in relationship to one another; write an equation to express one quantity, thought of as the dependent variable, in terms of the other quantity, thought of as the independent variable. Analyze the relationship between the dependent and independent variables using graphs and tables, and relate these to the equation. - MATH.CONTENT.6.EE.A.2.C
Evaluate expressions at specific values of their variables. Include expressions that arise from formulas used in real-world problems. Perform arithmetic operations, including those involving whole-number exponents, in the conventional order when there are no parentheses to specify a particular order (Order of Operations).