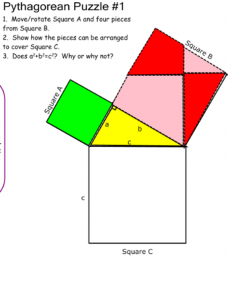
This learning progression was designed primarily for a slower pace 9th-grade geometry course. The Common Core State Standards that will be satisfied are from two different domains. The first two standards come from the cluster titled, “Understand and apply the Pythagorean Theorem,” these are 8.G.B.6 and 8. G.B.7. The second two content standards come from the cluster titled, “Define Trigonometric ratios and solve problems involving right triangles,” which are HSG.SRT. C.6 and HSG.SRT. C.8. In this course, students focus on mastering 8th grade standards as they slowly incorporate high school content standards. Throughout this learning progression, students will focus on four mathematical practices which are MP1, MP3, MP4, and MP6.
The curriculum these students are going through comes from the 2011 Holt McDougal Larson Geometry textbook. For this learning progression, students are beginning a brand-new unit on right triangles and trigonometry. Specifically, applying the Pythagorean Theorem and its converse to classify types of triangles along with students being able to identify similar triangles and write ratios.
The central focus of this learning segment is an investigation of side lengths and angles in triangles to be able to find missing side lengths and being able to classify different types of triangles. The purpose of this content is to give students the mathematical tools to use to work with all types of triangles, especial right triangles. The underlying concepts are right triangles, Pythagorean theorem and its converse, and similarity of triangles. The simple knowledge in this learning segment includes the vocabulary relating to triangles, such as right triangles, and the definitions of all components to the Pythagorean Theorem and its converse. The procedure of this learning segment is for students to learn how to apply the Pythagorean Theorem to find the length of the third side in a right triangle, and then being able to use the Converse of the Pythagorean Theorem to decide if the three given side lengths form an acute, right, or obtuse triangle. After being able to find missing side lengths and being able to classify triangles students will be able to explore ratios of side lengths of similar triangles. All leading to students developing enough mathematical reasoning to apply their knowledge to real-world mathematics. Throughout each lesson, I will use the data on prior academic learning and disposition from my observations and the series of entry tasks students turned in to support my students’ learning. I sequenced my learning targets to start with familiar learning targets and branched to learning goals that depended on a mastery of the previous ones. Breaking down the learning objectives is beneficial to students with need of support or accommodations, since focusing students’ attainment of immediate goals, such as getting today’s problem correct increases student self-efficacy according to A. Wade Boykin and Pedro Noguera’s book titled “Creating the Opportunity to Learn.”
Complete Learning Progression: Geometry Formatted Learning Progression FINAL