Author: sanchezesa
Painted Cube F.LE.A
The image can be use to teach students to create exponential functions, arithmetic series, description of the relationship of the different colors. Students make a list of the patterns in the cubes to help them create an equation that represent each of the cubes; to expand their thinking, they can create an equation that would give how many cubes of a given color depending on the area of the cube or the number of cubes used. To make the activity more engaging, providing students with wooden squares to recreate this image, would help students deepen their understanding of the problem. The image can be to teach ratios/proportions between objects.
HSF.LE.A.2
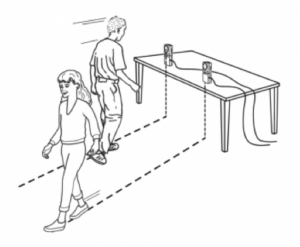
Where Do We Meet? REI
WHERE DO WE MEET?
Where do we meet is an interactive activity that uses technology and mathematical concepts to create and solve real life scenarios. One of the Vernier products to compliment this lesson is the Motion Detector. This device allows for data to be collected through a calculator (or a computer software) where students can then analyze their findings. For this activity students will be able to see a real life scenario of the usage of the mathematical concept of Solving Systems of Liner Equations using a motion detector, calculator and themselves. In this activity, students will be able to part of the creation of data that will be used to create equations. Students will then take part in solving the system of equations using technology and on writing (mathematically). Students will be able to use this activity that ties to the following Common Core State Standards:
INQB.2 Collect, analyze and display data using calculators, computers, or other technical devices when available
APPD.2 Use computers, probes, and software when available to collect, display, and analyze data.
M3.2.H Formulate a question that can be answered by analyzing data, identify relevant data sources, create an appropriate data display, select appropriate statistical techniques to answer the question, report results, and draw and defend conclusions.
H.A.REI.1– Explain each step in solving a simple equation as following from the equality of numbers asserted at the previous step, starting from the assumption that the original equation has a solution. Construct a viable argument to justify a solution method.
H.A.REI.2– Solve simple rational and radical equations in one variable, and give examples showing how extraneous solutions may arise.
H.A.REI.5– Prove that, given a system of two equations in two variables, replacing one equation by the sum of that equation and a multiple of the other produces a system with the same solutions.
H.A.REI.6– Solve systems of linear equations exactly and approximately (e.g., with graphs), focusing on pairs of linear equations in two variables.
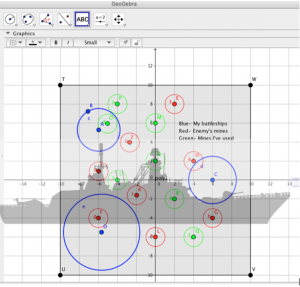
Battleships and Mines HSG.GPE
What better way to learn math than by playing Battleships and Mines!!!
This interactive activity will indulge your students into creating their own battleships and mines using geometry. Students will generate their battleships and mines using equations of circles that will be graph using GeoGebra. GeoGebra is a free and useful software where students can create circles with just two clicks! No more “I do not want to graph this!” With GeoGebra students will be able to fully engage in the activity while practicing the properties of the equation of a circle, without the hassle of graphing it. GeoGebra not only does it have functions that can be incorporated with algebra and calculus curriculum, but it comes at no cost to schools, teachers and students.
battleships-lesson-geometry-m325