By: Kimberly Younger, Rachel Van Kopp, Lizzie Englehart and Naomi Johnson
This lesson is focused on a 7th grade standard CCSS.Math.Content.7.G.B.6 but could be used for 6th through 8th grade depending on the application. This lesson focuses on the use of formulas to find area and problem solving of a real-world problem with the use of technology.
The prompt is “The school district is building a new playground for the new elementary school down the road. They have hired Playgrounds R’ Us to build it, but the supervisor wants to know what students would want on a playground. Create a playground with the following requirements.”
The students are building on their knowledge of area and perimeter formulas and applying it to a problem. The students are given a square footage for the playground, they must use three or more different shapes to represent their equipment, and the total square footage of the equipment must cover 30% of the playground’s area or more.
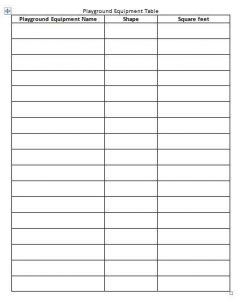
The students are given a packet which includes direction, a rough draft grid paper, final draft grid paper (submitted for approval), a screen shot of their Geogebra playground and a write up about their playground.
Below is an example of the packet students received. (link to the packet)
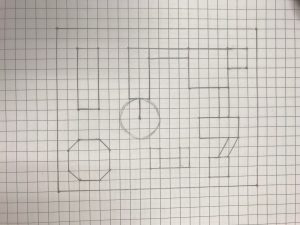
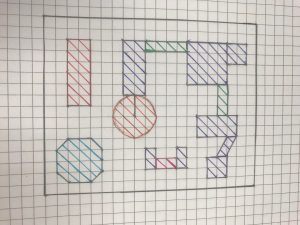
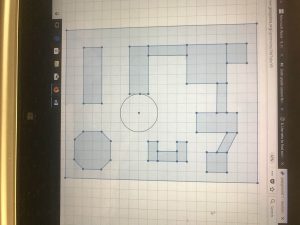
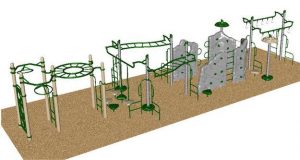
Below is a student’s sample playground
Rough Draft Blueprint Final Draft Blueprint Geogebra Blueprint
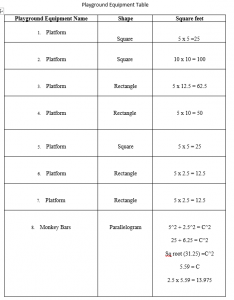
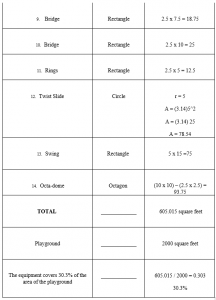
Table for Blueprint
Extension for “Build a Playground”:
As an extension to this lesson, students will later be able to work with 3 dimensional figures and nets to build the playground they have constructed in our lesson. This lesson emphasized finding and working with area of various geometrical figures and special reasoning. Using the knowledge, they have gained through our lesson, the students will be able to create the net that would best fit the equipment shape that they have presented to us on their “blue prints”.
In order to create the appropriate net, students will need to understand that the 3-dimensional shapes base will be the shape they have placed on their map in the lesson “Build a Playground”. This extension will cover CCSS.math.content.7.g.b.6 which states “Solve real-world and mathematical problems involving area, volume and surface area of two- and three-dimensional objects composed of triangles, quadrilaterals, polygons, cubes, and right prisms.” This extension will help students make connections to the relationships between 2-dimensional figures and 3-dimensional figures, and connect the concepts of surface area and volume to real-world scenarios.




 numerous more lessons involving it, and is especially useful for any movement-based projects/lessons that a teacher plans to do.
numerous more lessons involving it, and is especially useful for any movement-based projects/lessons that a teacher plans to do.